Technologies and Service
SNK has a wide range of efficient technological solutions in the field of repair and drilling of wells, enhanced oil recovery and oil production intensification.
Depending on the purpose of work, well conditions, the composition of reservoir water, temperature and many other factors SNK specialists offer individual solutions that allow customers to increase the profitability of mining projects in the implementation of geological and technical measures.
Oil well is a solid capital cylindrical construction formed by excavation, its barrel length is much greater than its diameter, and human access is limited. Its upper part is called the mouth, the bottom part is the face, and the walls are wellbore.
An oil well is constructed in accordance with the basic requirements:
- to provide easy access to the bottom of the deep mechanisms and geophysical instruments;
- to prevent destruction of wells’ walls, ensuring reliable separation of all layers from one another (to avoid overflow of fluids from the formation);
- to seal the wellhead if it is necessary.
Oil well types:
|
Vertical
|
Horizontal
|
Directional
|
Multi-Lateral / Multibranch
|
|
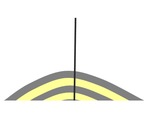
The angle of deviation is not more than 5° |
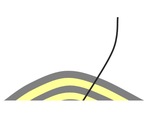
The angle of deviation is 80-90°. In this case, it is better to carry out the drilling of the wellbore along a seam. |
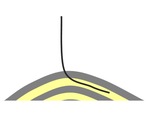
The angle of deviation is more than 5° |
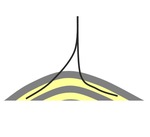
There is a main wellbore and secondary (or several). The difference is in the location of points of branching. Multilateral well has the point above the producing horizon. Multibranch well has the point of branching within the productive horizon |
Categories of oil wells:
|
Prospecting Wells |
Exploratory Wells |
Production Wells |
|
drilling for identification of new oil and gas deposits |
drilling in areas with existing oil and gas content to specify oil and gas deposits; data collection and clarification for the future projects on the development of new deposits. |
– firm wells (output and input); – reserve wells; – control wells (observation, piezometric); – evaluation wells; – special wells (water intake, absorbing, etc.); – offset wells. |
Output wells extract oil and natural gas, gas condensate and other associated components. There are the following types of wells:
- flow well;
- pump well;
- gas-lift well.
Input wells impact on the reservoirs by injection of water, gas and steam, as well as other working agents, into the wells. There are the following types of wells:
- perimeter well;
- edge well;
- intracotour well.
Reserve wells involve individual lenses, pinching zone and stagnant zones in the development. These zones are not involved in the development within their placement, in the categories of firm wells.
Control Wells:
- observation well is used for periodic monitoring of changes in the state of the water-oil, gas-water, gas-oil contacts, change of water and gas saturation of a reservoir;
- piezometric well is used for regular measurement of the pressure in the reservoir, perimeter area, oil-bearing zone, the gas cap.
Evaluation wells specify parameters and modes reservoirs’ operation, identify and clarify the boundaries of separate productive fields, analyze production of oil deposits of the autonomous regions.
Special wells are used for extraction of process water, gas storage, release of produced waters, killing of open flows. There are the following types of wells:
- water intake wells provide water supply during well drilling and maintenance of pressure of reservoir under development;
- absorbing wells are used for injecting of produced waters in the relative layers, from the fields under development.
Offset wells replace the wells of the firm fund which are abandoned due to wear-out, or for some other technical reasons.
See also:
Killing of wells
Drilling of oil and gas wells